CLP #2: Einstein’s Riddle
| Code | GitHub |
|---|---|
| Part 1 | What is CLP? |
| Part 3 | Scheduling Problem |
| Part 4 | Optimization Problem |
Introduction
Each of us knows that Albert Einstein was a great genius. His person had a huge impact on the development of physics, but have you ever heard of his riddle? If not then, I will explain it to you now.
Try to Solve It
There are five houses in five different colors. Each house is occupied by a man of different nationality. Each man has a different pet, prefers a different drink, and smokes different brand of cigarettes. The question is: who owns the fish?
There are the following hints:
- The Brit lives in the Red house.
- The Swede keeps dogs as pets.
- The Dane drinks tea.
- The Green house is next to the White house, on the left.
- The owner of the Green house drinks coffee.
- The person who smokes Pall Mall rears birds.
- The owner of the Yellow house smokes Dunhill.
- The man living in the centre house drinks milk.
- The Norwegian lives in the first house.
- The man who smokes Blends lives next to the one who keeps cats.
- The man who keeps horses lives next to the man who smokes Dunhill.
- The man who smokes Blue Master drinks beer.
- The German smokes Prince.
- The Norwegian lives next to the Blue house.
- The man who smokes Blends has a neighbour who drinks water.
Now you can try to solve this task yourself. Just in case, similar puzzles can be found here.
CLP Strength
If you do not know what Constraint Logic Programming is yet, I invite you to read my previous post. The main task will be to transform all assumptions into equations and inequalities. The other elements will be similar to the previous example.
Let’s start by collecting and segregating all the names appearing in the riddle. One way is to create several enums that will illustrate our problem more.
enum Pet { DOGS , BIRDS, HORSES, CATS, FISH }
enum Drink { TEA, COFFEE, MILK, BEER, WATER }
enum Color { RED, GREEN, WHITE, YELLOW, BLUE }
enum Nation { ENGLISHMAN, SWEDE, DANE, NORWEGIAN, GERMAN }
enum Cigarette { PALLMALL, DUNHILL, BLUEMASTER, PRINCE, BLEND }
enum OrderOfCategories { COLOR, NATION, PET, DRINK, CIGARETTE }
After that, we can make a special place for our variables and define constants: SIZE and DIST_1 (described below).
Store store = new Store(); // Store for CLP variables
ArrayList<IntVar> vars = new ArrayList<IntVar>(); // ArrayList of CLP variables to store all sets
final int SIZE = 5;
final IntVar DIST_1 = new IntVar(store, 1, 1);
We’ll also create several IntVar arrays. In the loop, for each index of each array, we can define the domain (possible value obtained) from 1 to 5 and add this element to the ArrayList. We’re doing it because every animal can belong to one of the five houses. The situation is similar for drinks, colors, nationalities and cigarettes.
IntVar pet[] = new IntVar[SIZE];
IntVar drink[] = new IntVar[SIZE];
IntVar color[] = new IntVar[SIZE];
IntVar nation[] = new IntVar[SIZE];
IntVar cigarette[] = new IntVar[SIZE];
// Determination of possible values
for (int i = 0; i < SIZE; i++) {
pet[i] = new IntVar(store, Pet.values()[i].toString(), 1, SIZE);
drink[i] = new IntVar(store, Drink.values()[i].toString(), 1, SIZE);
color[i] = new IntVar(store, Color.values()[i].toString(), 1, SIZE);
nation[i] = new IntVar(store, Nation.values()[i].toString(), 1, SIZE);
cigarette[i] = new IntVar(store, Cigarette.values()[i].toString(), 1, SIZE);
vars.add(pet[i]);
vars.add(drink[i]);
vars.add(color[i]);
vars.add(nation[i]);
vars.add(cigarette[i]);
}
Now the most important part of the program, that is imposing constraints. To somehow ensure that no pet, drink, color, nationality or cigarettes will be assigned to the same house, we should use Alldifferent(). I think the other constraints are understandable and logical. Only the constant DIST_1 mentioned above needs explanation. The answer is in the documentation - each parameter passed to the function must be of type IntVar. Therefore, we can not enter “1” (int) in distance() constraint.
// Constraints
store.impose(new Alldifferent(pet));
store.impose(new Alldifferent(drink));
store.impose(new Alldifferent(color));
store.impose(new Alldifferent(nation));
store.impose(new Alldifferent(cigarette));
store.impose(new XeqY( nation[Nation.ENGLISHMAN.ordinal()], color[Color.RED.ordinal()] )); // 1
store.impose(new XeqY( nation[Nation.SWEDE.ordinal()], pet[Pet.DOGS.ordinal()] )); // 2
store.impose(new XeqY( nation[Nation.DANE.ordinal()], drink[Drink.TEA.ordinal()] )); // 3
store.impose(new XplusCeqZ( color[Color.GREEN.ordinal()], 1, color[Color.WHITE.ordinal()] )); // 4
store.impose(new XeqY( color[Color.GREEN.ordinal()], drink[Drink.COFFEE.ordinal()] )); // 5
store.impose(new XeqY( cigarette[Cigarette.PALLMALL.ordinal()], pet[Pet.BIRDS.ordinal()] )); // 6
store.impose(new XeqY( color[Color.YELLOW.ordinal()], cigarette[Cigarette.DUNHILL.ordinal()] )); // 7
store.impose(new XeqC( drink[Drink.MILK.ordinal()], 3 )); // 8
store.impose(new XeqC( nation[Nation.NORWEGIAN.ordinal()], 1 )); // 9
store.impose(new Distance( cigarette[Cigarette.BLEND.ordinal()], pet[Pet.CATS.ordinal()], DIST_1 )); // 10
store.impose(new Distance( cigarette[Cigarette.DUNHILL.ordinal()], pet[Pet.HORSES.ordinal()], DIST_1 )); // 11
store.impose(new XeqY( cigarette[Cigarette.BLUEMASTER.ordinal()], drink[Drink.BEER.ordinal()] )); // 12
store.impose(new XeqY( nation[Nation.GERMAN.ordinal()], cigarette[Cigarette.PRINCE.ordinal()] )); // 13
store.impose(new Distance( nation[Nation.NORWEGIAN.ordinal()], color[Color.BLUE.ordinal()], DIST_1 )); // 14
store.impose(new Distance( cigarette[Cigarette.BLEND.ordinal()], drink[Drink.WATER.ordinal()], DIST_1 )); // 15
Finally, we can look for a solution. You can also easily calculate how much it takes to find a solution for a computer.
// Time - start
long T1 = System.nanoTime();
// Search for solution
Search label = new DepthFirstSearch();
SelectChoicePoint select = new InputOrderSelect(store, vars.toArray(new IntVar[1]), new IndomainMin());
label.labeling(store, select);
// Time - stop
long T2 = System.nanoTime();
System.out.println("Time: " + Long.toString(T2-T1) + "ns");
So Who Owns the Fish?
Returning to the main question, let’s find out about it by launching the program.
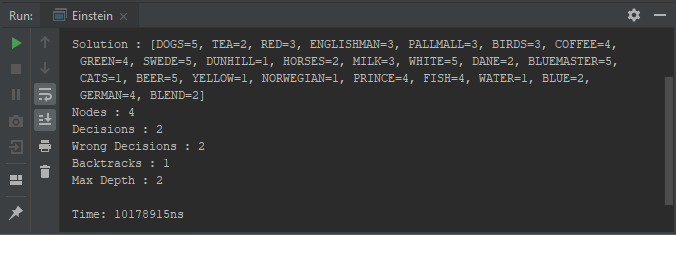
The owner of the fish is German. We can also see that the time it takes to find the right answer was \(10178915ns=0,01s\). In case of problems, the entire program can be found here. Did you manage to be faster than your computer?






Leave a comment